Law Offices of Sanders L. Denis|Criminal Defense Lawyer

1-718-766-9007
8005 Roosevelt Avenue, Suite 200, Jackson Heights, NY 11372
Family-Lawyer
FAMILY LAW LAWYER
NEW YORK
FAMILY LAW LAWYER
NEW YORK
We provide legal representation in a wide range of family court matters to defend you and help you protect your rights and the rights of your loved ones. We understand the traumatic legal sitution you may be facing.
Family Law Lawyer
New York
The Family Court hears matters involving children and families. It has the authority to make legal decisions over the following types of cases:
Custody: when a parent has custody of a child, he has the right to make important decisions for the child and is responsible for the physical care and supervision of the child.
Visitation:
when a parent does not have custody of a child, the Family Court may order the visit. The court can issue orders on visits until the child turns 18.
Child Support Attorney
Spousal and/or Child support:
child support and spousal support are payments ordered by the Family Court. Parents must support a child until the age of 21 and married people must support each other for as long as they are married.
Paternity Lawyer Queens, NY
Paternity:
paternity means that a man is the biological father of a child and has the legal right to custody and visits and is responsible for paying child support.
If you are looking for an Adoption lawyer
in New York, we represent clients in the New York courts.
Adoption: Adoption is the legal process where one or two people become the parent of a child and take the child to be their own. Once the adoption is approved, the adopted child has all the same rights as if he or she had been naturally born to the adoptive parents and the adoptive parents have all the rights and responsibilities of the biological parents.
For an adoption to be legally binding, all the laws and procedures must be strictly followed. Depending on the facts of your particular case, the adoption procedure can be complex.
Divorce Lawyer in the New York Supreme Court
Divorce: divorce cases are filed in the Supreme Court.
The Family Court hears matters involving
Abused or Neglected Children (Child Protective Proceedings)
Domestic Violence (Family Offense)
Juvenile Delinquency
Crimes Committed by Children Between 7-18
Starting at age seven, children can be brought to court if they are accused of committing a crime. Where the case is handled and how the child is treated depends on a number of factors including the child’s age, intent and past record. Youth who are accused of committing crimes fall into three categories: Juvenile Delinquent, Juvenile Offender, and Adolescent Offender.
Juvenile Delinquents
A Juvenile Delinquent is a child over 7, but under 18 years of age (effective 10/1/19), who commits an act that would be a crime if it had been committed by an adult. Juvenile offenders, who are 13, 14, and 15 years of age, are not considered Juvenile Delinquents. Cases involving Juvenile Delinquents are handled in Family Court. Juvenile Delinquents do not go to adult jails. Instead, the court decides if they need supervision, treatment or placement through the local department of social services or the New York State Office of Children and Family Services. Juvenile Delinquents do not have criminal records. Family Court proceedings are confidential and in some instances the cases can be sealed.
Queens Law Lawyer New York
Youthful Offender Defense Family Court
Effective 10/1/2019:
16 and 17-year-olds charged with misdemeanors under the penal law are considered Juvenile Delinquents and their cases are decided in the Family Court.
16 and 17-year-olds charged with misdemeanors under the Vehicle and Traffic
Law are considered adults and their cases are decided in the local criminal court.
16 and 17-year-olds charged with felonies are considered Adolescent Offenders and, if their cases are removed from the Youth Part in Supreme or County Court to Family Court, they will then be considered Juvenile Delinquents.
Juvenile Offenders
A child who is 13, 14, or 15-years-old and is charged with committing a serious or violent felony offense listed in Penal Law 10.00 (18), is considered a Juvenile Offender. These cases are heard in the Youth Part of the Supreme or County Court. Juvenile Offenders who are convicted after a plea or a trial are subject to less severe sentences than adults. Juvenile Offenders who are convicted will have a permanent criminal record unless the Court grants Youth Offender status.
Youthful Offenders
Youthful Offender status allows a youth to avoid the consequences of a permanent criminal record. To be eligible, the Youth must be at least 14 and less than 19 years of age. At sentencing, the Court determines whether or not to grant Youthful Offender status. If the Court grants it, the criminal conviction is replaced by the Youthful Offender status and the youth will no longer have a criminal record. Learn more about Youthful Offenders.
Adolescent Offenders
As of October 1, 2019, a 16 or 17-year-old who commits a felony is an adolescent offender. This means that the case is originally heard in the Youth Part of the Supreme or County Court. However, the case may be transferred to the Family Court, where the youth will be considered a juvenile delinquent and will be eligible to receive all the services and programs available to all juvenile delinquents. Learn more about Adolescent Offenders.
Raise the Age
As of October 1, 2019, New York State has raised the age of criminal responsibility to 18. This legislation is commonly referred to as the “Raise the Age” law. The “Raise the Age” law also created new Youth Parts and a new adolescent offender category.
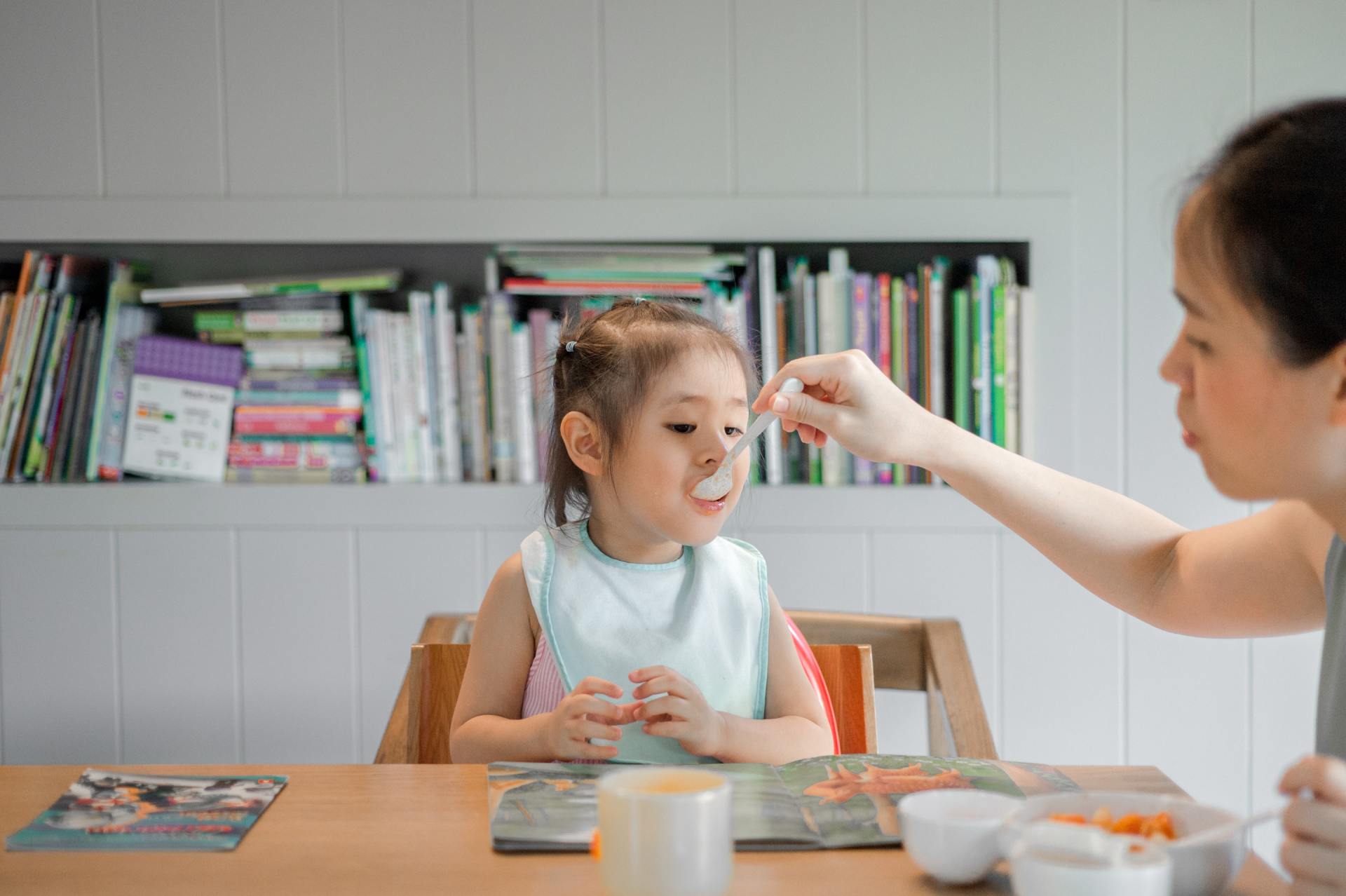

Child Support Lawyer
Child Support %
One Child 17%
Two Children 25%
Three Children 29%
Four Children 31%
Five + Children no less than 35%
Button
New York Child Custody Attorney
A New York court can make orders about the child's custody only until the child is 18 years old. The Court gives custody based on the "best interest of the child.
Button
Call For A ConsultaionLlame Para Una ConsultaHire An Experienced Lawyer For An Agressive Defense
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Bronx Criminal Lawyer
Write your caption hereButton
Abogado Defensa Criminal Queens
Write your caption hereButton
Law Offices of Sanders L. Denis | Criminal Federal Immigration Lawyer
All Locations
Criminal Immigration Family Lawyer in New York City
About Us
We have been providing expert legal counsel to clients for more than 28 years
News:
New York Times, Telemundo, Univision, New York Post, AP, NY1, CBS, New City Patch,
Contact Us 24/7
The information on this website is for advertising purpose only. Attorney Advertising. Nothing on this website and or associated pages, documents, comments, videos, answers or emails or other form of communication should be taken as legal advice for an individual case or situation.
